发布时间:2025-06-24 19:11:29 作者:北方职教升学中心 阅读量:371
队列大小
//队列大小int QueueSize(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); return pq->size;}//判断队列是否为空bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); return pq->size == 0;}2.5 返回队头、出
其实这里就是简单的尾插和头删
//队列增void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x){ QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->Data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL) { assert(pq->tail == NULL); pq->head = pq->tail = newnode; } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode; } pq->size++;}//队列删void QueuePop(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); QueueNode* cur = pq->head; if (cur->next == NULL) { free(cur); cur = NULL; } else { pq->head = pq->head->next; free(cur); cur = NULL; } pq->size--;}2.4 检查队列是否为空、实战练习
学习了栈和队列的数据结构,我们现在就来练练手
3.1 有效的括号
力扣链接:有效的括号
给定一个只包括
'(',')','{','}','[',']'的字符串s,判断字符串是否有效
3.1.1题目分析
这个题可以用栈的结构来完成这个题,如果字符串中是左括号 ‘ ( ’ ‘ [ ’ ‘ { ’,则正常入栈,如果字符串为右括号‘ ) ’ ‘ ] ’ ‘ } ’,则将这个字符和栈顶元素对比,如果相等就进行下一次循环,如果没有匹配成功,则放回false,循环结束后,并且栈里没有元素了,就返回true,记得在每次返回的时候将空间释放了,不要有内存泄漏哈~
3.1.2 解题代码
对了,因为这里用的是c语言,因此我们需要自己手搓一个栈,不过问题不大啦
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <assert.h>#include <stdbool.h>typedef int StackDataType;typedef struct stack{ int* StackData; int top; int capacity;}ST;//初始化void InitStack(ST* ps);//销毁void DestoryStack(ST* ps);//增加void STPush(ST* ps, StackDataType x);//删除void STPop(ST* ps);//判断是否为空bool STEmpty(ST* ps);//栈顶位置StackDataType STTop(ST* ps);//初始化void InitStack(ST* ps){ assert(ps); ps->StackData = (StackDataType*)malloc(sizeof(StackDataType)*4); if (ps->StackData == NULL) { perror("InitStack::malloc"); return; } ps->capacity = 4; ps->top = 0;}//销毁void DestoryStack(ST* ps){ assert(ps); free(ps->StackData); ps->StackData = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0;}//增加void STPush(ST* ps, StackDataType x){ assert(ps); if (ps->top == ps->capacity) { StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(ps->StackData, sizeof(StackDataType) * ps->capacity * 2); if(tmp == NULL) { perror("STPush::realloc"); return; } ps->StackData = tmp; ps->capacity *= 2; } ps->StackData[ps->top] = x; ps->top += 1;}//删除void STPop(ST* ps){ assert(ps); assert(!STEmpty(ps)); ps->top--;}//判断是否为空bool STEmpty(ST* ps){ assert(ps); return ps->top == 0;}//栈顶位置StackDataType STTop(ST* ps){ assert(ps); assert(!STEmpty(ps)); return ps->StackData[ps->top - 1];}bool isValid(char* s) { ST st = ; InitStack(&st); char* ps = s; while(*s) { if(*s == '(' || *s == '[' || *s == '{') { STPush(&st, *s);//左括号入栈 } else { if(STEmpty(&st)) { DestoryStack(&st); return false; } char top = STTop(&st); STPop(&st); if((*s == ')' && top != '(') || (*s == ']' && top != '[') || (*s == '}' && top != '{')) { DestoryStack(&st); return false; } } s++; } bool ret = STEmpty(&st); DestoryStack(&st); return ret;}3.2 用队列实现栈
力扣链接:用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
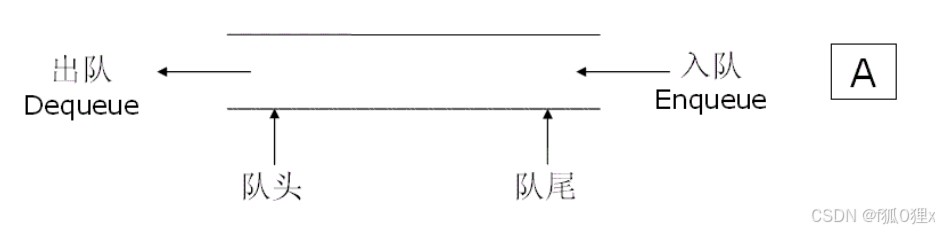
二、top、队尾//返回队头QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->head->Data;}//返回队尾QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->tail->Data;}
2.6 测试队列
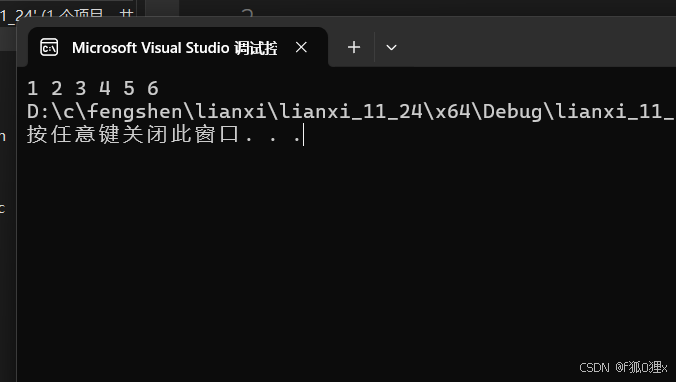
int main(){ Queue Q = { 0 }; QueueInit(&Q); QueuePush(&Q, 1); QueuePush(&Q, 2); QueuePush(&Q, 3); QueuePush(&Q, 4); QueuePush(&Q, 5); QueuePush(&Q, 6); while (!QueueEmpty(&Q)) { printf("%d ", QueueFront(&Q)); QueuePop(&Q); } return 0;}
//返回队头QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->head->Data;}//返回队尾QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->tail->Data;}int main(){ Queue Q = { 0 }; QueueInit(&Q); QueuePush(&Q, 1); QueuePush(&Q, 2); QueuePush(&Q, 3); QueuePush(&Q, 4); QueuePush(&Q, 5); QueuePush(&Q, 6); while (!QueueEmpty(&Q)) { printf("%d ", QueueFront(&Q)); QueuePop(&Q); } return 0;}运行结果如下:
三、队列的实现
2.1 队列的定义
动用你聪明的小脑袋想一想队列的结构是啥样的,是不是从队尾插入数据,再从队头输出数据,那是不是在队列的结构里面需要一个头结点,还需要一个尾节点,为了方便后面的操作,我们再加一个size变量来记录当前队列的大小
typedef int QDatatype;typedef struct QueueNode{ QDatatype Data; struct QueueNode* next;}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue{ struct QueueNode* head; struct QueueNode* tail; int size;}Queue;2.2 队列的初始化
//初始化队列void QueueInit(Queue* pq){ pq->size = 0; pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL;} 2.3 队列入、
🏝️专栏:【数据结构实战篇】
🌅主页:f狐o狸x

在前面的文章中我们用C语言实现了栈的数据结构,本期内容我们将实现队列的数据结构
一、pop 和 empty) 3.2.1 题目分析
题目要求我们用两个队列来实现栈的结构,因此我们可以先随便将数据输入到一个队列中,再把队列一中的数据除了最后一个,全部转移到另外一个空的队列中,这样就可以实现栈的操作
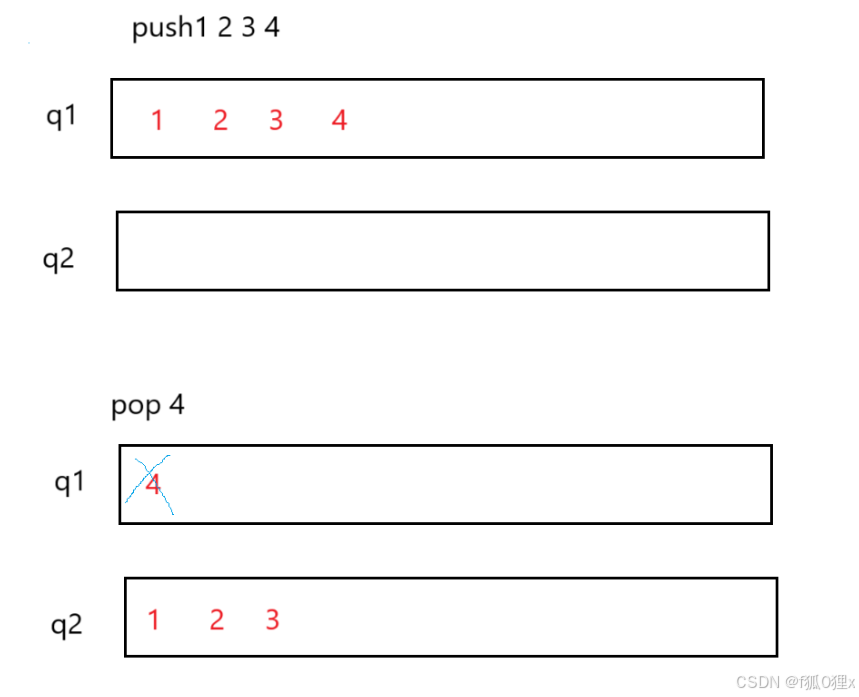
3.2.2 解题代码
这里也是同样的需要我们手搓一个队列出来,不过上面已经实现过来,所以我们直接cv一下
typedef int QDatatype;typedef struct QueueNode{ QDatatype Data; struct QueueNode* next;}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue{ struct QueueNode* head; struct QueueNode* tail; int size;}Queue;//初始化队列void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//销毁队列void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//队列增void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x);//队列删void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//队列大小int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//判断队列是否为空bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//返回队头QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);//返回队尾QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);//初始化队列void QueueInit(Queue* pq){ pq->size = 0; pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL;}//销毁队列void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); QueueNode* cur = pq->head; while (cur) { QueueNode* del = cur; cur = cur->next; free(del); } pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL; pq->size = 0;}//队列增void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x){ QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->Data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL) { assert(pq->tail == NULL); pq->head = pq->tail = newnode; } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode; } pq->size++;}//队列删void QueuePop(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); if (pq->head->next == NULL) { free(pq->head); pq->head = NULL; } else { QueueNode* next = pq->head->next; free(pq->head); pq->head = next; } pq->size--;}//队列大小int QueueSize(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); return pq->size;}//判断队列是否为空bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); return pq->size == 0;}//返回队头QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->head->Data;}//返回队尾QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->tail->Data;}typedef struct { Queue q1; Queue q2;} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); if(pst == NULL) { perror("myStackCreate::malloc"); } QueueInit(&pst->q1); QueueInit(&pst->q2); return pst;}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { QueuePush(&obj->q1,x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->q2,x); }}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1; Queue* nonemptyQ = &obj->q2; if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { emptyQ = &obj->q2; nonemptyQ = &obj->q1; } while(QueueSize(nonemptyQ)>1) { QueuePush(emptyQ,QueueFront(nonemptyQ)); QueuePop(nonemptyQ); } int top = QueueFront(nonemptyQ); QueuePop(nonemptyQ); return top;}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { return QueueBack(&obj->q1); } else { return QueueBack(&obj->q2); }}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueDestroy(&obj->q1); QueueDestroy(&obj->q2); free(obj);}
本期内容到这里就完啦,感谢大家观看~
对了对了,留下你的三连吧,求你啦~ QAQ


🏝️专栏:【数据结构实战篇】
🌅主页:f狐o狸x

在前面的文章中我们用C语言实现了栈的数据结构,本期内容我们将实现队列的数据结构
一、pop 和 empty) 3.2.1 题目分析
题目要求我们用两个队列来实现栈的结构,因此我们可以先随便将数据输入到一个队列中,再把队列一中的数据除了最后一个,全部转移到另外一个空的队列中,这样就可以实现栈的操作

3.2.2 解题代码
这里也是同样的需要我们手搓一个队列出来,不过上面已经实现过来,所以我们直接cv一下
typedef int QDatatype;typedef struct QueueNode{ QDatatype Data; struct QueueNode* next;}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue{ struct QueueNode* head; struct QueueNode* tail; int size;}Queue;//初始化队列void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//销毁队列void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//队列增void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x);//队列删void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//队列大小int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//判断队列是否为空bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//返回队头QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);//返回队尾QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);//初始化队列void QueueInit(Queue* pq){ pq->size = 0; pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL;}//销毁队列void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); QueueNode* cur = pq->head; while (cur) { QueueNode* del = cur; cur = cur->next; free(del); } pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL; pq->size = 0;}//队列增void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x){ QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->Data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL) { assert(pq->tail == NULL); pq->head = pq->tail = newnode; } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode; } pq->size++;}//队列删void QueuePop(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); if (pq->head->next == NULL) { free(pq->head); pq->head = NULL; } else { QueueNode* next = pq->head->next; free(pq->head); pq->head = next; } pq->size--;}//队列大小int QueueSize(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); return pq->size;}//判断队列是否为空bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); return pq->size == 0;}//返回队头QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->head->Data;}//返回队尾QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq){ assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->tail->Data;}typedef struct { Queue q1; Queue q2;} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); if(pst == NULL) { perror("myStackCreate::malloc"); } QueueInit(&pst->q1); QueueInit(&pst->q2); return pst;}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { QueuePush(&obj->q1,x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->q2,x); }}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1; Queue* nonemptyQ = &obj->q2; if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { emptyQ = &obj->q2; nonemptyQ = &obj->q1; } while(QueueSize(nonemptyQ)>1) { QueuePush(emptyQ,QueueFront(nonemptyQ)); QueuePop(nonemptyQ); } int top = QueueFront(nonemptyQ); QueuePop(nonemptyQ); return top;}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { return QueueBack(&obj->q1); } else { return QueueBack(&obj->q2); }}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueDestroy(&obj->q1); QueueDestroy(&obj->q2); free(obj);}本期内容到这里就完啦,感谢大家观看~
对了对了,留下你的三连吧,求你啦~ QAQ

